Children typically start growing their first baby teeth around 6 months of age, and they continue to lose them and grow permanent teeth until about 12 years old. During this time, they’re especially vulnerable to early childhood caries. However, awareness and treatment of childhood dental caries lagged behind adult dental care for a long time, only improving after the economic boom of the 1980s. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at childhood tooth decay to improve prevention, catch it early, and provide the right treatment, all so that kids can have a healthy, beautiful smile.
1. What is Early Childhood Caries?
Early childhood caries (ECC) is a common bacterial infection that damages the teeth over time. After eating, food particles can get stuck between the teeth, causing dental plaque to form. The bacteria in the plaque then produce acid, which wears down the tooth enamel. Enamel is the protective layer of the tooth, and when it’s damaged, cavities begin to form. This is what we refer to as childhood caries.
2. What Causes Childhood Caries?
As discussed in our previous article, “Dental Caries Definition” dental caries is caused by four main factors: bacteria, the host (teeth), diet, and time. These same four factors are responsible for childhood caries, which leads to cavities in children’s teeth.
3. Why is Childhood a High-risk Period for Dental Caries?
There are three main reasons for this:
Poor oral hygiene
Before the age of three, many children’s primary teeth haven’t fully come through, and a lot of them don’t yet have the habit of brushing regularly. This means food particles stay in their mouths, allowing plaque to build up. Over time, this increases the chances of developing childhood caries.
Early symptoms not obvious
Primary teeth are smaller, and early childhood caries are often not noticeable. In many cases, dental pulp disease or periapical disease is diagnosed only after the problem becomes more severe. However, there’s no need to panic. If treated effectively, primary teeth decay will not affect the development of permanent teeth.
Tooth misalignment
During the transition from primary to permanent teeth, both sets coexist, teeth are not aligned, the bite is not correct, making it easier for food debris to accumulate. This increases the risk of childhood caries. As permanent teeth are crucial for long-term dental health, parents should be especially vigilant during this period.
4. What are The Behaviors of Your Baby That May Lead to Being Targeted More Easily by Caries?
**Here comes the point, parents please pay attention, try to avoid these behaviors will keep your baby away from childhood caries and have a healthy teeth.**
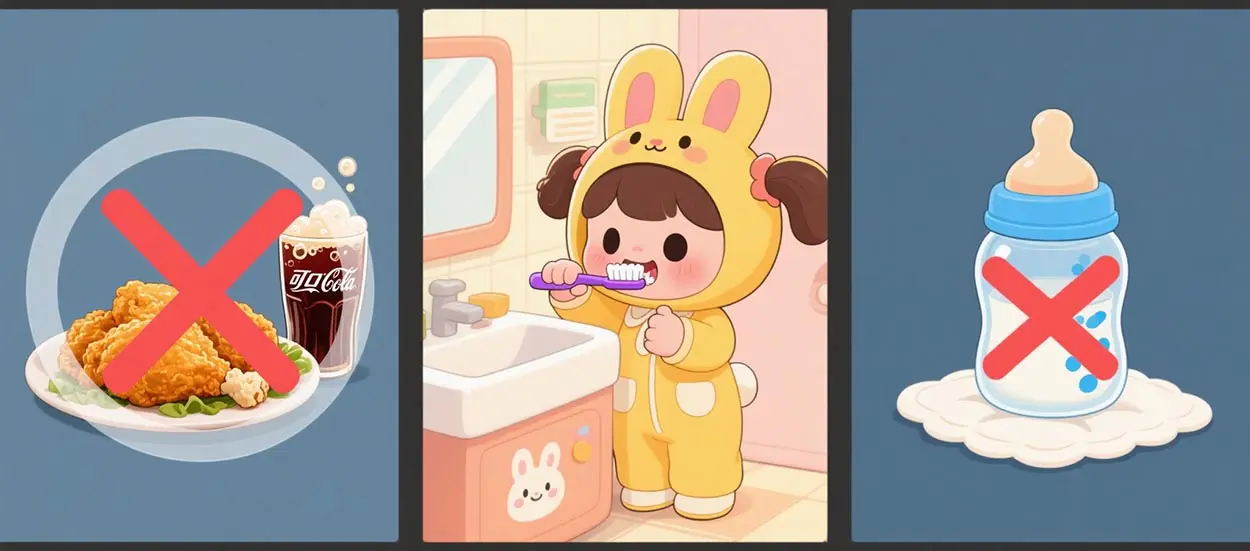
(1). Like high sugar and high oil food:
such as milk tablets, milk candy, fried chicken, cola and other foods. These foods are easy to remain in the mouth and stick to the crevices of the teeth and are difficult to remove. Especially cola itself is strongly acidic, too much drinking will directly destroy tooth enamel causing caries. For the health of your baby’s teeth, encourage them to eat more apples, celery and other foods rich in plant fiber. These fruits and vegetables are not only nutritious, but also natural toothbrushes, when chewing these foods can remove the residue in the crevices of the teeth, thus making it impossible for bacteria to survive, and there will be no caries crisis.
(2). Do not brush and clean teeth:
If the baby does not have the habit of regular brushing and cleaning teeth, it will lead to a large number of bacteria in the mouth, and over time will produce caries. To cultivate the baby from childhood love gargling, brushing teeth habit. After three years old, you can use soybean-sized fluoride toothpaste, which can better protect tooth enamel, so that children’s caries can not be.
(3). The teeth themselves are defective, the bite is not correct:
For example, infants with frequent night milk, like to bite the bottle to sleep baby, easy to cause baby teeth underbite. If this kind of malocclusion is not corrected in time, it is not only unattractive, but also easy to hide dirt and form childhood caries.

5. Symptoms of Dental Caries in Children
There is no obvious precursor to children’s dental caries. After the beginning of caries, there will be darkening of the teeth, sensitivity, and toothache after eating irritating foods. Different types of children’s dental caries may manifest as:
| Primary tooth caries: | multiple teeth suffering from caries at the same time, extensive caries, rapid progress. Symptoms are not obvious, and clinical complications into endodontics or periapical disease are common. |
|---|---|
| Young permanent tooth caries: | mostly seen in the first permanent molar, followed by maxillary middle incisor. Mostly acute, easy to evolve into endodontics, periapical disease |
6. What are The Possible Complications of Dental Caries in Children?
| Pulpitis: | If dental caries is not treated in time, the decay can penetrate through the dentin and develops into pulpitis, which will lead to impeded growth of permanent teeth. |
|---|---|
| Malnutrition: | caries leads to tooth loss, resulting in decreased chewing function, affecting food digestion and absorption, leading to malnutrition. The neuralgia by dental caries will also reduce the child’s appetite, leading to further deepening of malnutrition. Dental caries in children should therefore be taken very seriously and treated in a timely manner. |
7. Treatment Options for Children’s Dental Caries
Pre-caries:
- Remineralization treatment: Use of fluoride-containing preparations, proportional pastes of calcium, phosphorus and fluoride to restore hardness and remineralize enamel softened by pre-decay demineralization. This method can also be used to prevent caries in caries-susceptible children, so that caries in children can be nipped in the bud.
- Fossa sealing: Use polymer material to fill in the fossa of the children’s young permanent teeth, so that the surface of the teeth becomes smooth and easy to clean. On the one hand, after the fossa sealing, the original bacteria in the fossa are cut off from the source of nutrition and gradually die; on the other hand, the caries-causing bacteria from the outside can no longer enter, so as to achieve the purpose of preventing caries in the fossa.
- Drug treatment: drug treatment of caries is mainly applicable to shallow caries with extensive caries surface, inhibit the development of caries, but can not restore the shape of the tooth. Commonly used drugs for children are 2% sodium fluoride solution, 5% stannous fluoride, 4% fluorophosphate solution or gel, etc., the surface of the tooth is coated with moisture for about 4 minutes, and it is not suitable for rinsing and eating within 30 minutes, and it is coated once every half a year.
Surgical treatment of caries in the middle and late stages:
- Filling and restoration treatment: the soft tissues of the tooth that have eroded and decayed are surgically removed, the hard tissues of the tooth that have been decayed are defective, and the cavity is restored with filling and restoration techniques. The filling will cover the cavity so that the internal bacteria will be inactivated without a source of nutrients, thus terminating the progression of caries.
- Root canal therapy: When caries penetrates deep into the pulp, causing inflammation of the pulp and irreversible periapical lesions, root canal therapy is currently the most effective and commonly used treatment option.
8. Can Children Dental Caries Be Cured?
Caries in the primary teeth period can be cured after treatment without affecting the permanent teeth behind. If caries develops after tooth replacement, it can also be cured if it is in the early stages. After caries develops into a cavity, treatment can only restore chewing and appearance, and it’s not as good as the original teeth. Therefore, we should always pay attention to dental health, and the earlier caries is detected and treated.
9. How to Prevent Dental Caries in Children?
- Regular oral examination: early detection and treatment.
- Pay attention to diet: avoid eating too much high sugar, too hard food, eat more calcium and phosphorus rich, coarse grains and other foods rich in plant fiber.
- Cultivate good daily habits: don’t let your child form the habit of sleeping with a bottle to avoid “bottle caries”. After the age 2 should say goodbye to the pacifier, to avoid the primary teeth, malocclusion leads to dental caries. From childhood to cultivate the baby love hygiene habits, gargle after meals. Brush teeth and do not eat snacks before going to bed.

10. Conclusion
Children’s caries progress quickly, parents should pay enough attention to early detection and treatment as soon as possible in order to minimize the damage of caries on the teeth. If your baby’s teeth are already decayed, don’t need to worry too much, timely treatment can restore your baby’s chewing function and bright smile.
FAQs
Q1. Should caries in primary teeth be taken seriously?
Yes, although primary teeth will be replaced by permanent teeth, untreated caries in primary teeth can lead to infections that cause problems in the development of permanent teeth. In severe cases, it can affect your baby’s eating and digestive problems.
Q2. Can early childhood caries be reversed?
In the early stages of caries (white spot lesions), it can be reversed – with fluoride treatment and good oral hygiene.
Q3. What can I do to prevent dental caries if my child likes to drink juice milk?
Limit juice or milk intake to mealtimes and rinse or brush teeth after meals.
Q4. Is fluoride safe for my child?
Yes. Fluoride is both safe and effective in preventing tooth decay when used in the amounts recommended by your dentist.