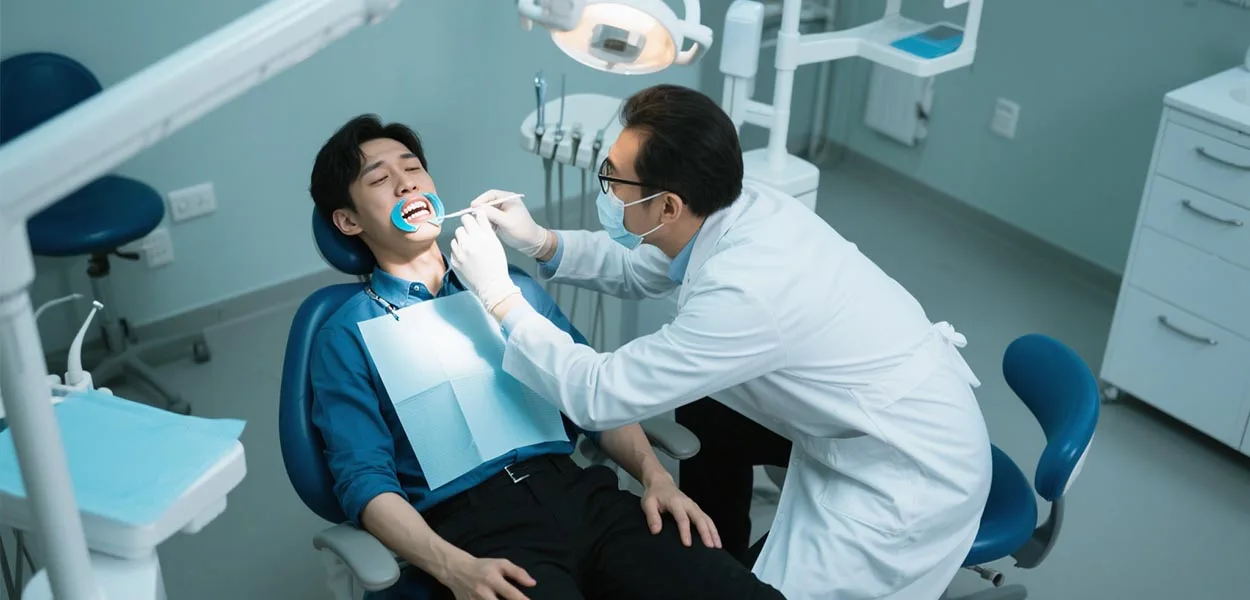
Introduction:
In orthodontic treatment, 90% of dentists rely on Cheek Retractors to enhance the operating field of view and patient treatment experience. Whether it is for invisible braces, dental implants or full-mouth orthodontic treatment, Cheek Retractors has become a key tool for improving efficiency and treatment accuracy. This article will deeply analyze the core functions of the oral expander to help dental clinics optimize the treatment process and enhance patient satisfaction.
1. Why Cheek Retractors has Become a Core Tool in Orthodontic Treatment?
A study in the American Journal of Orthodontics from 2023 shows that clinics using cheek retractors can save treatment time by 22% and increase patient satisfaction by 37%. These tools do more than just improve accuracy. They also make more comfortable that doing three key things:
1). Helps with Precision
cheek retractor can create 8–12mm space in the mouth, so doctors can see and work in areas like the second molars more easily.
2). Reduces Jaw Strain
The cheek retractor can helpe the mouth stay open without too much pressure, it reduces strain on the jaw joints.
3). Infection control optimization
FDA-certified medical stainless steel material to prevent cross-infection.
According to the latest report from the World Dental Federation (FDI), clinics using professional buccal extenders have shown the following data leaps:
- The error rate of treatment decreased by 41%
- Iatrogenic soft tissue injury reduced by 68%
- The daily number of patients at increased by 19%
It is worth noting that its application has broken through the traditional orthodontic field
- Implant surgery : Maintaining the stability of the buccal flap during immediate implant surgery
- Oral cancer screening : In conjunction with an endoscope, a panoramic view of the vestibular sulcus is achieved
- Pediatric dentistry : Combining behavioral management techniques to reduce the fear index of children.
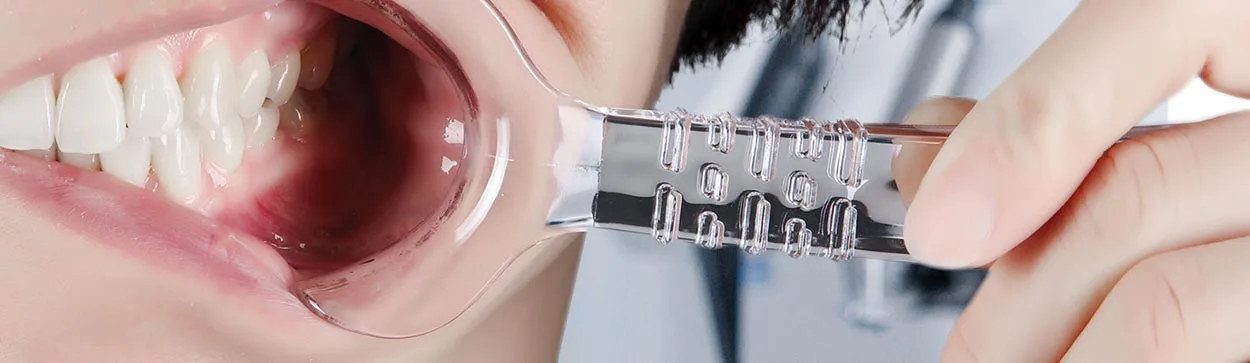
2. Comparison of the 4 Main Cheek Retractors Types
| Type | Applicable Scene | Material Features | Clinical Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adjustable for Children | Mixed dentition stage orthodontics | Silicone edging to prevent pressure marks | Adapts to the jaw development characteristics of children aged 4-12 |
| Universal Adult Type | Invisible aligner bonding | 304 stainless steel + anti-fog coating | Supports up to 15N without deformation |
| Single-Sided for Local Treatment | Local repairs/tooth treatment | Transparent PC material | 360° unobstructed light-curing operation |
| X-ray Specific Type | CBCT/X-ray imaging | Carbon fiber frame | Zero metal artifacts in imaging |
3. 4 Important Buying Tips for Cheek Retractors
- Ergonomic Design
Choose cheek retractors that with ADA (American Dental Association) Ergonomic Design Certification. These designs are made to reduce patient discomfort during long procedures. - Sterilization Compatibility
Make sure the retractor can handle high-pressure steam sterilization at 134°C, that is important for infection control. - Oral Cavity Fit
Choose retractors that can be adjusted to fit different mouth shapes, from children to old patients. - Material and Durability
Most cheek retractors are made from plastic, silicone, or metal. Choose one that is durable, easy to clean, and resistant to damage, so it use longer.

4. Advanced Techniques for Clinical Use
- Preoperative preparation : Apply vaseline to the corners of the mouth to avoid traction injury (especially for elderly patients)
- Angle adjustment : Maintain a 15° Angle between the extended plane and the occlusal plane to optimize the field of view
- Time management : If used continuously for more than 40 minutes, pause for 5 minutes to restore blood supply to the mucosa
- Postoperative disinfection: Pre-treatment brushing → multi-enzyme soaking (40℃/5min)→ ultrasonic cleaning (5MHz/8min)→ drying inspection → pre-vacuum sterilization (134℃/4min)

5. FAQ
Q: How do I know if the retractor is the correct size?
A: The device should sit 2-3mm away from the corners of the mouth when properly positioned. After placement, the entire premolar region should be fully visible without obstructions.
Q: How to avoid oral injury during the use of Cheek Retractors?
A: When using it for a long time, you can choose Cheek Retractors with a soft silicone inner lining and make sure to adjust its position regularly to avoid continuous pressure on the soft tissues of the oral cavity.
Q: Does the appearance of white spots after disinfection affect its use?
A: This is a residue of hard water. It can be removed by wiping with a 75% alcohol cotton pad and will not affect the performance of the instrument.
Q: What are the precautions for the maintenance of Cheek Retractors?
A: In addition to regular cleaning and disinfection, it is also necessary to regularly check whether the instruments have cracks or deformations to ensure their normal use and the safety of patients.
Conclusion
Cheek retractors are an essential tool to help improve dental treatment experience, not just adding to the accuracy and efficiency of the treatment, but also making the treatment a lot less painful for the patients. As technology in dentistry continues to advance, there are now more kinds and models of Cheek Retractors commercially available, providing physicians with various options to cater to various requirements during treatment.