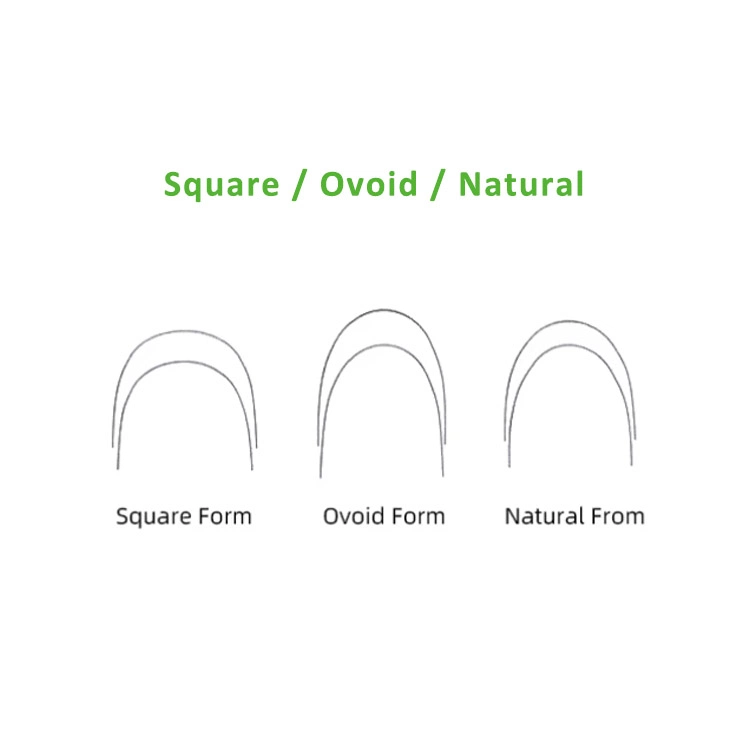

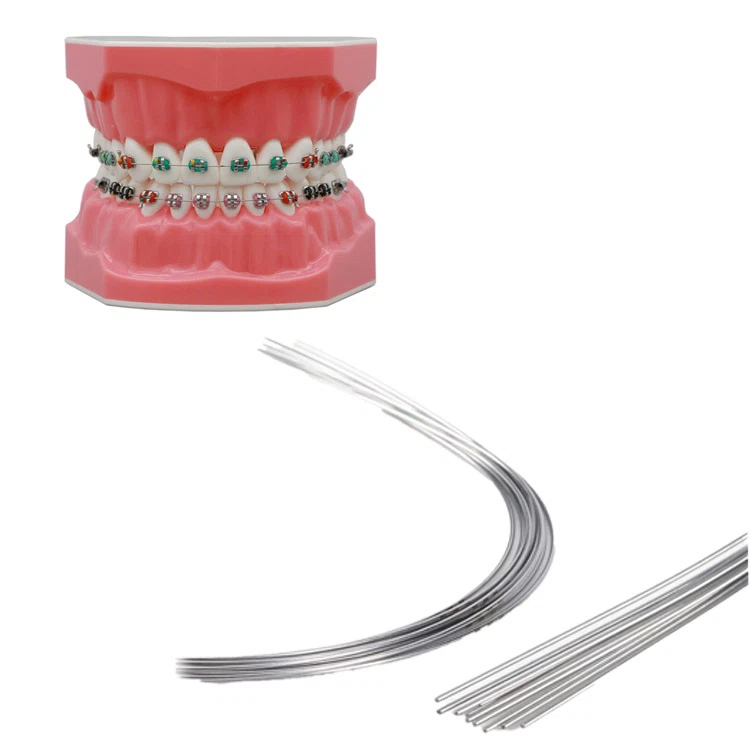

Kieferorthopädie -Bogendraht
- Niti / Edelstahlbogendraht
- Paket: 10PCs/Pack
- Zeigt ausgezeichnete Frühlingsrücken
- Konsequente Leistung
- Hoch poliert für verringerte Reibung
- Vollständige Seriengröße und Formulartyp für die Wahl
Der kieferorthopädische Bogendraht übt den Druck auf die Zähne aus, um sie dazu zu veranlassen, sich in eine festgelegte Position zu bewegen. Es wird normalerweise in Verbindung mit Zahnspangen verwendet, und durch Einstellen der Spannung und Richtung des Kieferorthopädiedrahtes, Es kann die Ausrichtung der Zähne effektiv verbessern und Probleme beißen.
Kieferorthopädische Bogendrähte tragen eine leichte kontinuierliche Spannung auf die Stütz- und Verankerungspunkte in den Zähnen auf. Diese Zähne bewegen sich subtil, doch allmählich über einen längeren Zeitraum, in die gewünschten Positionen verschieben. Das Ergebnis einer kieferorthopädischen Behandlung ist die Ausrichtung der Zähne, Symmetrische Zahnbögen, und eine Verringerung der Dünnheit zwischen den Zähnen, was die Gesichtskontur verändert, es harmonischer und ästhetisch ansprechender machen. Kieferorthopädische Bogendrähte glätten die Zähne und verbessern die Fähigkeit, mit einem besseren Biss zu kauen.
Kategorie Kieferorthopädie








Basierend auf der Materialzusammensetzung, Unsere kieferorthopädischen Erzwire können entweder Edelstahldrähte und Niti -Drähte klassifiziert werden. Während Edelstahlbogendraht billig ist und einen guten Abrieb und Korrosionsbeständigkeit aufweist und lange in der Mundhöhle Stabilität ist, Härte ist hoch, nicht so bequem wie Niti -Drähte, und geringe Elastizität. Niti -Bogendraht ist super elastisch und hat eine Formspeicherfunktion. Es ist flexibler, Ermöglichen, dass es besser auf die Zahnoberfläche passt, So macht es bequemer, aber zu einem höheren Preis.
Verwandte Produkte
The Definition of Orthodontic Arch Wires
Orthodontic arch wire is a key component in oral orthodontic treatment. It is a fine wire material with specific mechanical properties, mainly transmitting orthodontic force through the archwire bracket system, promoting the slow movement of teeth and adjusting the occlusal relationship. Throughout the entire treatment process, orthodontic wires play a dual role as both a “force conductor” and a “tooth guide”, and their performance directly affects the orthodontic outcome, treatment duration, and patient comfort.
Orthodontic arch wires are typically made of metal alloys, such as stainless steel wires composed of iron, chromium, and nickel; nickel-titanium alloy wires made from nickel and titanium; and beta-titanium alloy wires featuring a titanium base alloyed with elements like molybdenum and niobium.
Principle of Orthodontic Arch Wires
The orthodontic arch wire precisely transmits the orthodontic force preset by the doctor to the target tooth through its connection with the brackets (metal or ceramic bases adhered to the surface of the tooth, which are accessories for orthodontic treatment), generating a compressive force and thereby promoting the slow movement of the tooth within the alveolar bone. The ultimate goal is to achieve the therapeutic objective of straightening teeth, coordinating occlusal relationships and improving facial morphology.
Material Classification and Features of Orthodontic Arch Wires
1. Stainless steel wire
- Zusammensetzung: Mainly composed of metals such as iron, chromium, and nickel (chromium content: 17%-19%, nickel content: 8%-10%), some pro products also add elements such as molybdenum and titanium to optimize performance.
- Merkmale: Hohe Stärke, great rigidity, strong corrosion resistance, and less prone to rust in a moist oral environment. It has a moderate elastic modulus, which can provide stable orthodontic force and has good processing performance. It can be bent into various shapes of archwire according to the treatment requirements.
- Applicable stage: It is often used in the middle and later stages of orthodontic treatment, such as fine adjustment after teeth alignment and correction of occlusal relationship, and is particularly suitable for cases with high requirements for orthodontic efficiency.
2. Nickel-titanium alloy wire
- Zusammensetzung: A shape memory alloy composed of nickel (50%-55%) and titanium (45%-50%), it can be classified into austenitic nickel-titanium wire and martensitic nickel-titanium wire according to its crystal structure.
- Merkmale: It has shape memory effect and super elasticity, can return to the preset shape at body temperature, and continuously provide gentle and stable corrective force. It has a low elastic modulus, causes less irritation to teeth, and improves patient comfort.
- Applicable stage: Mainly used in the early stage of treatment, such as aligned teeth and open occlusion, it is particularly suitable for cases with severe tooth crowding and torsion, effectively reducing the patient’s discomfort.
3. Titanium alloy wire (β -titanium alloy wire)
- Zusammensetzung: Alloys formed by adding elements such as molybdenum, niobium, and zirconium to titanium as the base material (such as Ti-Mo-Nb-Zr alloy).
- Merkmale: It combines the high strength of stainless steel wire with the good elasticity of nickel-titanium alloy wire, and its elastic modulus lies between the two. It has good biocompatibility and contains no nickel, making it suitable for patients allergic to nickel. It has strong corrosion resistance and good processing performance, and can be made into complex bow wire shapes.
- Applicable stage: It is suitable for the middle stage of orthodontic treatment, especially during the transition period from aligned teeth to fine adjustment. It can not only provide sufficient corrective force but also ensure the stability of tooth movement.
The Types of Orthodontic Arch Wires Corrective Forces
According to the nature of the force generated by orthodontic arch wires, they are mainly classified into the following types:
- Elastic force: When orthodontic arch wires undergo elastic deformation, elastic force is generated, which is the main source of power for tooth movement. Nickel-titanium alloy wire has the gentlest, most stable and longest-lasting elastic force, while stainless steel wire has stronger elastic force but a relatively shorter duration.
- Friction: The friction between orthodontic wires and brackets has a significant impact on the speed of tooth movement. During the stage of aligning teeth, it is necessary to minimize friction as much as possible to enhance the efficiency of movement. During the fine adjustment stage, appropriate friction helps maintain the stable position of the teeth.
- Torque force: The torque force generated by bending the orthodontic arch wire can control the lip and tongue tilt of the teeth, improving the occlusal relationship and facial shape. Titanium alloy wire has good torque force stability and is a commonly used torque control material in clinical practice.
Factors Affecting the Orthodontic Force of Orthodontic Arch Wires
- Material properties: The elastic modulus, yield strength and elastic limit of different materials vary, which directly determine the magnitude and duration of the corrective force. Zum Beispiel, nickel-titanium alloy wire has a low elastic modulus, resulting in a relatively small corrective force but a longer duration. Stainless steel wire has a high elastic modulus, providing a relatively large corrective force but a short duration.
- The diameter of orthodontic wires: The diameter of the wires is a key factor affecting the orthodontic force. The larger the diameter, the higher the strength and the greater the corrective force. The smaller the diameter, the better the elasticity and the smaller the corrective force. The commonly used diameter specifications include 0.012 Zoll, 0.014 Zoll, 0.016 Zoll, 0.018 Zoll, 0.020 Zoll, usw.
- The shape of the arch wire: The shape of the arch wire (such as circular, square, or rectangular) affects the contact area with the bracket and the friction force, thereby influencing the transmission of orthodontic force. The circular wire has a small contact area and low friction, making it suitable for the stage of tooth alignment. Square and rectangular wires have a large contact area, which can more effectively transmit torque force and are suitable for the fine adjustment stage.
Precautions for Orthodontic Arch Wires
- Maintain oral hygiene: After the orthodontic arch wire is connected to the brackets, food debris is prone to accumulate. If not cleaned in time, it may lead to the accumulation of dental plaque, which in turn can cause problems such as tooth decay and gingivitis.
- Avoid chewing hard objects: The strength and wear resistance of orthodontic wires are limited. Chewing hard objects (such as nuts, bones, hard candies, ice cubes, usw.) may cause the wires to break, deform or the brackets to fall off, affecting the treatment progress.
- Regular follow-up visits: Patients need to have regular follow-up visits as required by the doctor (Normalerweise alle 4 Zu 8 Wochen), so that the doctor can adjust the diameter, shape or tension of the orthodontic arch wire according to the movement of the teeth.
- Pay attention to oral discomfort symptoms: After wearing orthodontic arch wires for the first time or making adjustments, patients may experience discomfort such as toothache or wear of the oral mucosa, which usually gradually subsides within 1 Zu 2 Wochen. If the discomfort persists or worsens, medical attention should be sought promptly for examination.
FAQs
There is no fixed standard for the frequency of orthodontic arch wire replacement. It mainly depends on the treatment cycle, the speed of tooth movement and the goals of the treatment stage. Normalerweise, during the entire orthodontic treatment (1.5 Zu 3 Jahre), orthodontic wires are replaced 4 Zu 8 mal.
Keep the broken part and contact your dentist. He will readjust or replace the orthodontic arch wire. Do not handle it by yourself to avoid the risk of accidental ingestion.
Gently clean the area around the archwire and brackets with an interdental brush, and use a water flosser to remove food debris.
Ja. After orthodontic treatment is completed, the dentist will remove all orthodontic arch wires, brackets and other components from the mouth at the last follow-up visit. After removal, he will clean and polish the surface of the teeth. It is recommended to wear retainers to maintain the stable position of the teeth and prevent them from rebounding.
The core selection principles (biocompatibility and matching treatment goals) are consistent, but due to the different dental and periodontal conditions of children and adults, there are detailed differences.




