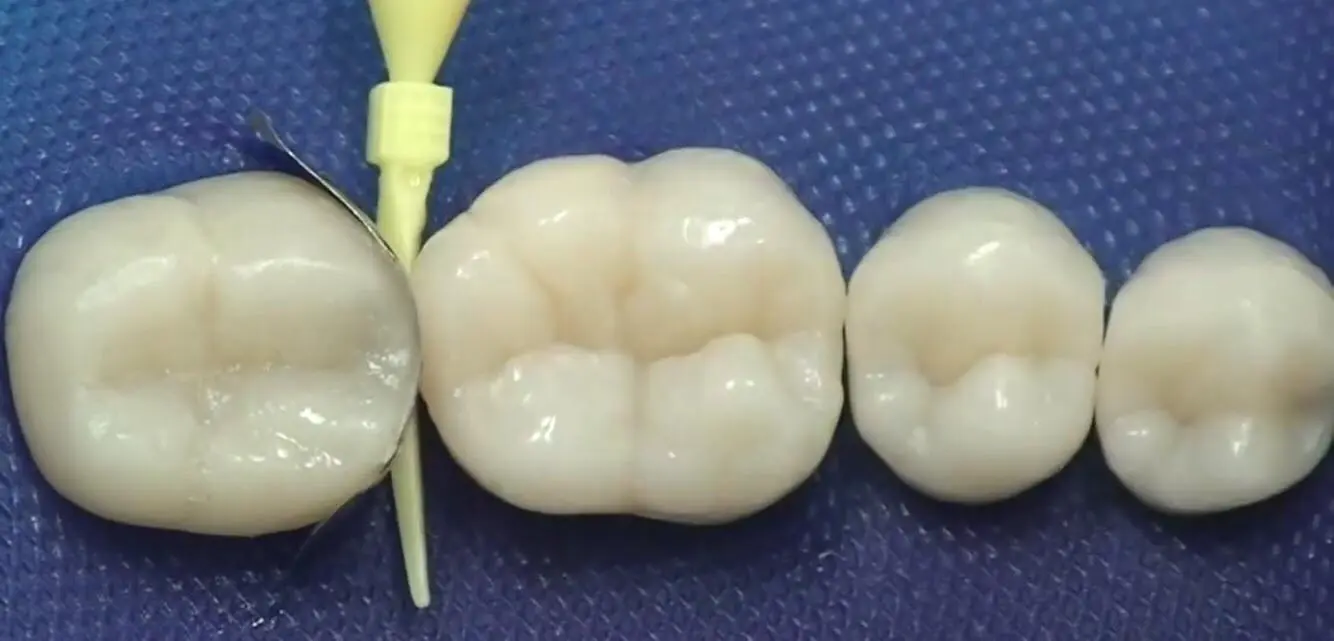
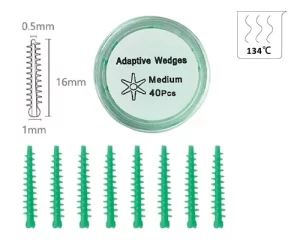
Anche se piccolo, I cunei dentali svolgono un ruolo insostituibile nell'odontoiatria restaurativa. Sono usati principalmente per la separazione dei denti, stabilizzare le bande di matrice e modellare i bordi dei restauri. A seconda del materiale e del design, Le prestazioni cliniche e l'uso di zeppe variano. In questo articolo, analizzeremo sistematicamente i tipi di zeppe dentali, le loro proprietà materiali, le loro funzioni principali e la loro applicazione in riempimento e restauro.
1. Tipi di zeppe dentali e proprietà del materiale
Zeppe dentali di plastica
Materiale: Spesso fatto di polipropilene medico (Pp), flessibile.
Vantaggi:
- L'elasticità moderata riduce la pressione sulle gengive.
- Può essere sterilizzato ad alte temperature ed è adatto al riutilizzo.
Svantaggi:
- Supporto limitato, non è adatto per i casi con Carie profonda o lacune strette.
Display campione:
- Guardie per zeppe dentali (GD-5675): con buco con rblade
Tre dimensioni: Grande/medio/piccolo

- zeppe adattive (GD-5677): con un nucleo di plastica interiore ferma, coperto di silicone

- zeppe dentali in resina (GD-5678): quattro dimensioni, XS/S/M/L.

- spicchi di diamanti (GD-5679): Sette dimensioni, X-Small/piccolo/medio/grande/profondo/l-medio/l-large

- Zeppe Tulwar (GD-5680): Tre dimensioni, Piccolo/medio/grande

Zeppe dentali di legno
Materiale: Per lo più betulla o pino, sterilizzato. Betulla si incastra con un contenuto d'acqua di 12% può espandersi fino a 18.7% In 30 minuti in un ambiente fluido gengivale. Questa proprietà adattiva li rende particolarmente adatti per i casi di recessione gengivale nei vecchi pazienti. Tuttavia, Si dovrebbe fare attenzione: L'eccessiva espansione può portare a una pressione eccessiva sulla membrana parodontale, innescare la sensibilità postoperatoria.
Vantaggi:
- Naturalmente assorbente d'acqua e gonfiore, Meglio adattarsi al gap intraoperatorio.
- Rigido, Adatto per un supporto ad alta resistenza delle cavità di classe II.
Svantaggi:
- Inutilizzabile, L'eccessiva espansione può causare disagio.
Display dei campioni:

Altri tipi
- Cuneo di metallo: Raro, comunemente usato per la preparazione completa della corona o scenari di restauro speciali.
- Cuneo di silicone: morbido e flessibile, Adatto per restauri estetici, Ma più costoso.
2. Le tre funzioni fondamentali del cuneo del dente
Separazione dei denti
- Separa temporaneamente i denti vicini 0.2-0.5 mm con forza meccanica leggera per creare uno spazio operativo.
- Ciò impedisce al ripristino di sporgere e ripristina la forma naturale dei punti vicini.
- Studi clinici hanno dimostrato che l'uso corretto dei cunei può ridurre il rischio di impatto alimentare fino a 60%.
Stabilizzazione della banda a matrice
- I cunei dentali possono aiutare a fissare il pezzo di stampaggio, prevenire la perdita del materiale restauro e modellare il contorno ideale.
- Restauri di cavità II: la combinazione con il Bande di matrice La stabilizzazione è la soluzione classica.
- Restorazioni di Classe V di cavità: di solito in combinazione con una piastra di stampaggio curvo.
Gum protection and hemostasis
- Dental wedges can provide a certain degree of protection above the gums.
- After the dental wedge is inserted into the tooth, it will exert a slight pressure on the gum, reducing bleeding during the operation.
3. Application Skills in Filling and Repair
Come scegliere il cuneo giusto
| Criteri | Tipo di cuneo consigliato |
|---|---|
| Spazio interprossimale stretto | Zeppe di legno, it’s expand and fit together after getting wet |
| Ampio spazio interprossimale | Cuneo plastico, elastic fit |
| Resina attillata | Clear plastic wedges, facilitate light penetration |
| Riempimento di amalgama | Zeppe di legno, it can offer stronger support |
Insert the Angle and direction
The dental wedge should be inserted obliquely into the interdental space from the lingual or buccal side of the tooth, and the Angle should be controlled at 30° to 45°. The core purpose of this Angle design is to avoid the gum tissue, prevent direct compression or scratching of the gum during vertical insertion, and reduce the risk of postoperative gum redness, swelling and bleeding.
Insertion depth control
The top of the wedge should be slightly higher than the edge of the restoration by approximately 0.5mm. This reserved space is designed to compensate for the shrinkage during the curing process of subsequent filling materials (come resina), ensuring that the material can closely adhere to the edge of the tooth after curing and avoiding the formation of gaps that could lead to secondary caries.
Clinical precautions
Avoid excessive pressure on the gums: Durante l'operazione, the insertion force of the dental wedge should be controlled. Excessive pressure can damage the attachment relationship between the gums and the teeth, which may cause postoperative gum recession. Clinical statistics show that the incidence of such complications is approximately 3% A 7%.
Precise positioning of the insertion position: If the dental wedge is inserted at an offset position (such as being too close to the occlusal surface or the root tip direction), it may cause the contact points of adjacent teeth to be too loose, thereby affecting the stability of the normal occlusal relationship. Patients may experience problems such as weak bite and food impaction.
Actual case: Repair of deep wedge-shaped defect
Taking the repair of a deep wedge-shaped defect of the left lower first premolar as an example, the specific operation and therapeutic effect are as follows:
- Preoperative assessment: The patient was a 45-year-old adult. The cervical defect of the left lower first premolar had reached the deep dentin, accompanied by obvious cold and heat sensitivity symptoms. The Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) was used to assess the sensitivity degree, with a score of 6/10.
- Key operation techniques: Primo, use the No. 00 gingival line for gingival drainage treatment. Poi, insert a pre-moistened pine wedge and let it stand for 15 minutes until it fully expands to widen the tooth gap. Prossimo, fluid resin is used as the base, and then 3M Z350XT resin is used for layered filling. The wedges should be retained until the resin has initially cured before being removed to prevent material deformation during the filling process.
- Postoperative efficacy: The patient was followed up for one year after the operation. The examination showed that the integrity rate of the restoration reached 98%, with no loosening, detachment or secondary caries. The patient’s cold and heat sensitivity symptoms completely disappeared, and the occlusal function returned to normal.
4. Purchasing Criteria for Dental Wedges
Priorità di sicurezza dei materiali
Core certification standards
The material and sterilization treatment of the wedge must comply with professional medical standards. Different materials correspond to clear certification requirements:
- Zeppe di plastica: Must have FDA (Food and Drug Administration of the United States) or CE (European Union Product Safety Certification) medical-grade polymer certification. The core needs to avoid harmful substances such as phthalates, which may migrate through contact and pose potential health risks. Compliance certification is the key basis for ensuring the safety of materials.
- Zeppe di legno: A complete EO (ethylene oxide) sterilization report must be provided, and the report should clearly state that the biological load is ≤10⁻⁶ (i.e., the probability of microbial survival after sterilization does not exceed one in a million), ensuring that there are no pathogenic bacteria remaining before use to avoid cross-infection or postoperative inflammation.
Key points to avoid pitfalls in procurement
Quando si acquista, be cautious of non-medical grade products and especially reject “industrial wooden wedges” without any marking. Most of these products are made from leftover materials from industrial processing and have not undergone medical-grade treatment. They may contain harmful chemicals such as formaldehyde. When used, they not only easily irritate the gum tissue but may also be absorbed through the oral mucosa, posing a threat to the patient’s health. Inoltre, there are no unified standards for their size and hardness, which cannot meet the precise operation requirements of dental restoration.
Maximize the size fit rate
When choosing wedges, it is necessary to combine the actual clinical needs and maximize the size fit rate through “preoperative assessment + multi-specification reserve”.
Before the operation, the size of the required wedge should be initially determined based on the width of the interdental gap of the affected tooth (such as the interdental caries gap, wedge-shaped defect gap) and the tooth morphology (such as deciduous teeth and permanent teeth, normal teeth and inclined teeth).
It is recommended to stock up on multiple sizes of wedges (such as thin, medio, spesso, or thin and thick styles for special tooth gaps) to avoid poor fit due to insufficient single size, which may affect the gap opening effect or cause gum compression. This ensures that a matching model can be found for different cases, improving operational efficiency and restoration quality.
5. Conclusione
Although dental wedges are small in size and seem insignificant, they are indispensable “key supporting roles” in dental restoration operations. From material selection to standardized use, precise control over every link is not only the core guarantee for enhancing the stability of the restoration and reducing postoperative complications, but also can effectively improve the patient’s diagnosis and treatment experience and lay a foundation for a long-term good prognosis.