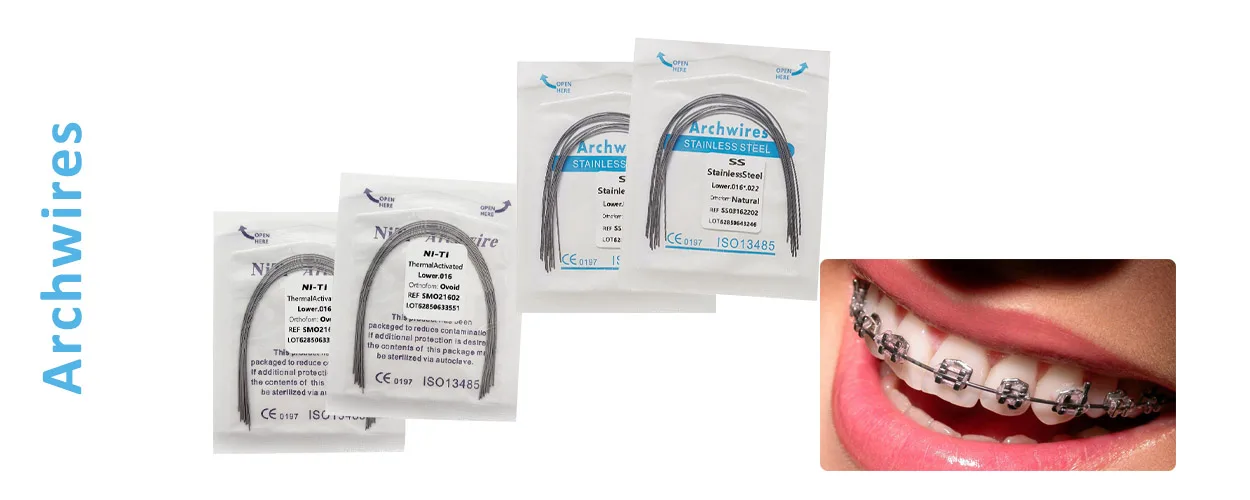
En tratamiento de ortodoncia, Archwire es uno de los componentes centrales del sistema de corrección del soporte. Si eres un ortodoncista o un líder de compras dental, Este artículo analizará las características técnicas., Escenarios de aplicación y sugerencias de compra de arcos de ortodoncia desde una perspectiva profesional, ayudándole a igualar sus necesidades clínicas de manera más eficiente.
1. ¿Qué son los arcos de ortodoncia??
Thin, flexible metal wires that are fastened to dental brackets are called orthodontic archwires. Con el tiempo, these wires gradually shift the teeth into the proper position by applying light, continuous pressure. These wires are known as “arch wires,” and the lower arch is formed by the wires on the lower teeth, while the upper arch is formed by the wires on the upper teeth.
Actúan como un motor guía para los dientes y son esenciales para controlar el movimiento del diente. Sin él, Tus dientes torcidos nunca se moverían. Estos alambres de frenos vienen en diferentes tamaños y tienen diferentes composiciones de materiales..
2. ¿Cuál es la función de los arcos??
As a dynamic mechanical component of the orthodontic system, the orthodontic archwires achieves passive movement of teeth through an accurate compression mechanism. During the initial treatment stage, orthodontiologists select nickel-titanium alloy archwires with appropriate elastic modulus. Their shape memory properties can apply a continuous orthodontic force of 0.5 to 1.5N/cm² to the misaligned dentition. This mechanical stimulation triggers alveolar bone remodeling by activating the proliferation of osteoclasts on the pressure side and osteoblasts on the tension side, achieving a monthly displacement of 0.1 to 1mm for the teeth.
Los arcos realizan tres funciones esenciales:
| Guía vectorial | Establecer la curvatura ideal del arco dental a través de la conformación de alambre preformado |
| Entrega de fuerza | Traducir las limitaciones del sistema de soporte al movimiento direccional del diente |
| 3D Control | Ajuste de la inclinación axial y el posicionamiento de rotación a través de la ingeniería de torque |
The dynamic adjustment mechanism runs through the entire treatment cycle: follow-up is conducted every 4 a 6 semanas, and orthodontists maintain the optimal orthodontic force of 20 to 150g/cm by replacing the archwire. In the middle and later stages of treatment, it transitions to the stainless steel archwire stage (0.016×0.022 inches to 0.019×0.025 inches), with an elastic modulus of 210GPa. This enables the establishment of an accurate three-dimensional mechanical system, allowing for fine regulation of root tip movement and occlusion.
Profit’s three-stage theory (Profit, Campos, & Sarver, 2018) is followed by this biomechanical system: initial alignment → vertical control → torque fine-tuning, which leads to 80–90% repositioning of the dental arch and functional occlusal reconstruction. According to clinical data, the archwire system’s standardized application can maintain the root resorption rate below the safe threshold (< 2mm) and boost orthodontic treatment efficiency by 40%.
3. La ciencia detrás de los arcos de ortodoncia
Today’s archwire is an engineering marvel, in contrast to orthodontics’ homogeneous approach in the early 20th century. Materials science holds the key to their success: the right alloy selection has a direct impact on treatment speed, comfort, and result.
Consider NiTi (nickel-titanium) wire. Almost no one anticipated that NiTi would have dental potential when Dr. William J. Buehler first noticed its “shape memory” qualities in the Naval Research Laboratory in the 1960s. These days, this alloy is a major solution to the issue of crowded teeth because it can “remember” the patient’s ideal dental arch shape and can withstand up to 8% strain (whereas steel can only withstand 1%).
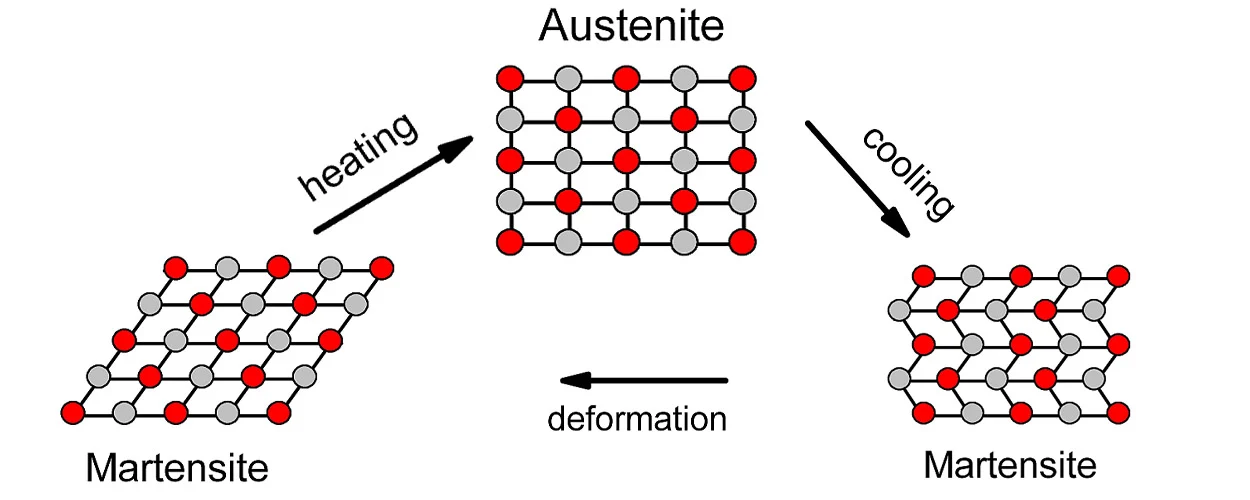
4. Clasificación de arcos de ortodoncia
Orthodontic archwires can be classified into three major types based on the different material properties:
A. Arcos de níquel-titanio (Niti)

B. Archwire de acero inoxidable

DO. Archwire beta-titanio

5. Criterios de selección clínica para arcos de ortodoncia
Match elasticity to strength according to the treatment stage
For initial correction, superelastic nickel-titanium archwires should be given priority to reduce patient discomfort. In the middle and later stages, stainless steel or β -titanium bow wires are replaced to precisely control the force.
Focus on the surface treatment process
High-quality bow wires should have a smooth surface (such as electrochemical polishing) to reduce the friction of the brackets and avoid mucosal irritation.
Standardized dimensions and memory performance
Select archwires that meet the AAO (American Orthodontic Association) standards to ensure compatibility with mainstream bracket systems and high shape memory stability.
6. Clinical Usage and Maintenance Suggestions
- The archwire replacement cycle: The patient’s tooth movement speed and the level of orthodontic archwires fatigue determine how often it is adjusted, which is typically every 6 a 8 semanas.
- Advice for patients: Keep in mind to refrain from chewing hard objects, apply orthodontic wax to ease any initial discomfort caused by friction, and clean the archwire on a regular basis to avoid plaque buildup.
- Storage requirements: To prevent oxidation or deformation, unopened bow wires should be kept in a dry atmosphere.
7. Por qué elegir nuestro Arcos de ortodoncia?
Como exportador especializado en la investigación y desarrollo de consumibles dentales para 15 años, Ofrecemos:
Control de calidad estricto: Los productos son ISO 13485 certificado, FDA/CE compatible y rastreable por lotes.
Elecciones diversificadas: cubriendo el rango completo de tamaños de 0.012 ″ a 0.021 × 0.025 ″, Apoyo a la personalización multimaterial como el níquel-titanio, acero inoxidable, beta-titanio y así sucesivamente.
Intercambio de casos: Solución de alambre de proa para mejorar la eficiencia de la clínica.

Una cadena de clínicas dentales en Barcelona, España, redujo el ciclo de tratamiento promedio de los casos iniciales por 15% y el tiempo para los ajustes de seguimiento de 20% mediante el uso de nuestros arcos nitinol. La retroalimentación del médico es que "la estabilidad de la memoria de forma del Archwire reduce significativamente la complejidad de la operación, que es especialmente adecuado para pacientes adolescentes ".
Conclusión
Despite their small size, orthodontic archwires are essential components that influence the correction effect. Selecting the appropriate archwire can boost patients’ confidence in the course of treatment in addition to increasing the effectiveness of diagnosis and treatment. Please do not hesitate to contact us at any time if you would like free samples or more information about our products.
Referencias
- Cha, S. J., Ali, METRO., & Matthews, METRO. mi. (2015). Materiales y técnicas de ortodoncia. Revista de Ortodoncia Clínica, 49(8), 23-34.
- Ribeiro, T. K. S. J., Silva, S. A. S., & Da Silva, D. PAG. (2020). Mecanismos biológicos del movimiento de los dientes: Una revisión. Revista Europea de Ortodoncia, 42(2), 55-64.
- Profesor, W. R., Campos, H. W., & Sarver, D. METRO. (2018). Ortodoncia contemporánea (6la ed.). Elsevier.