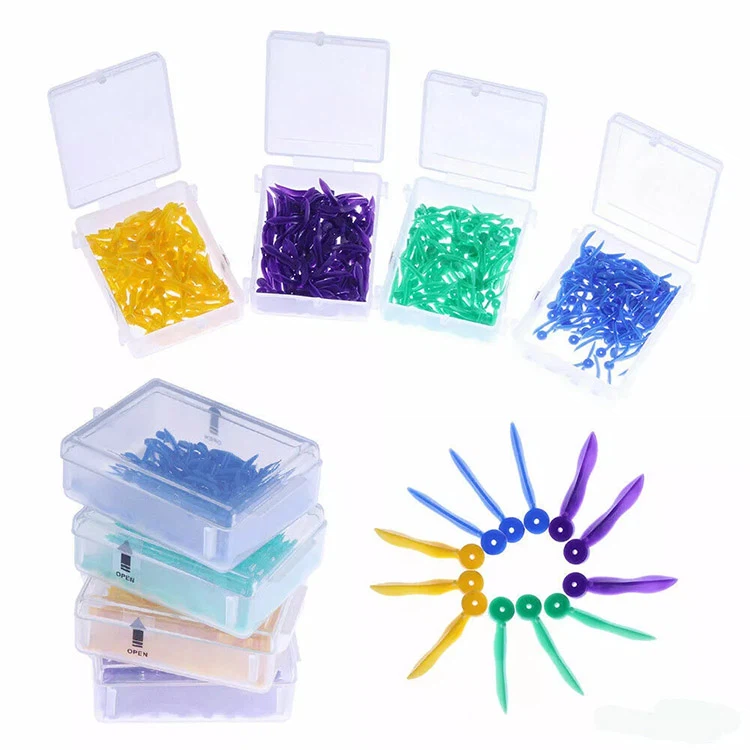
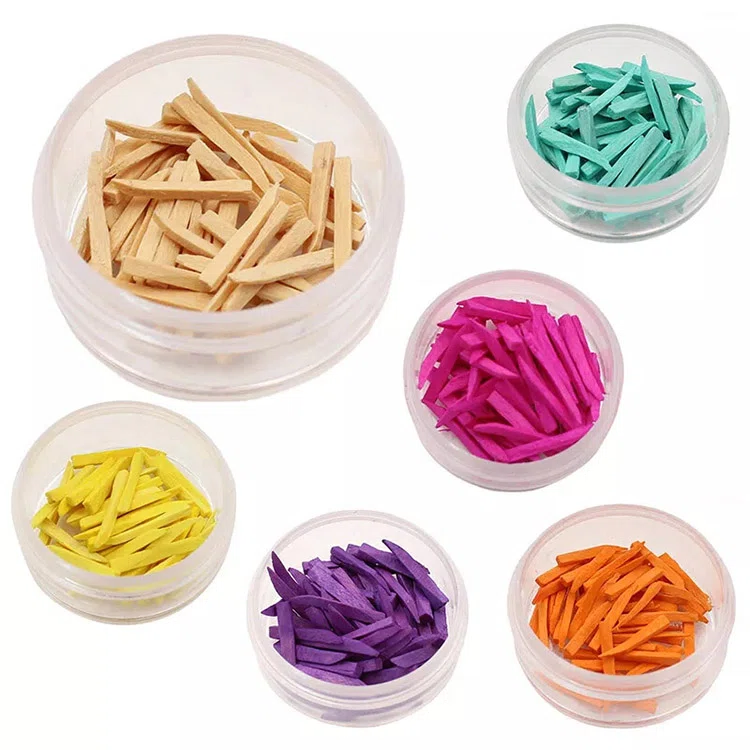
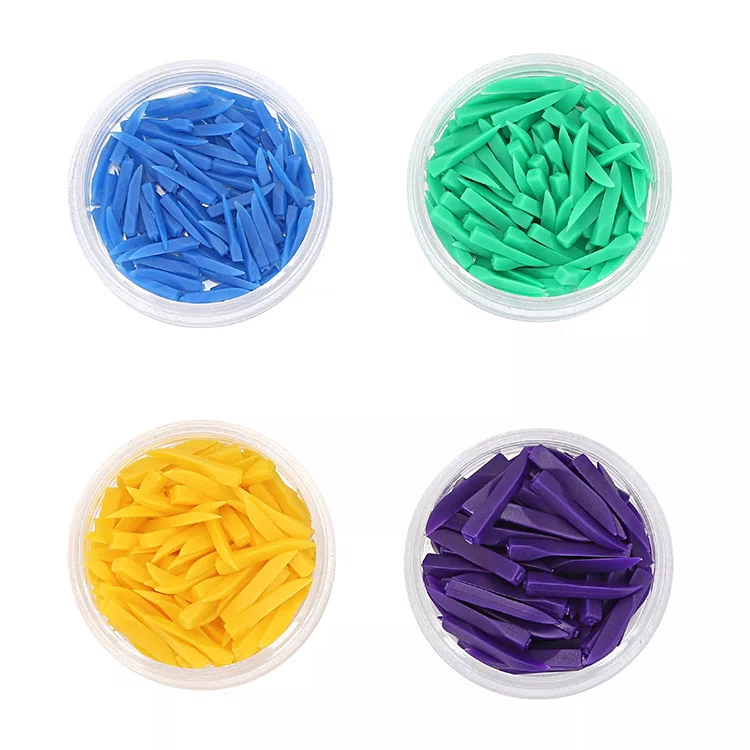
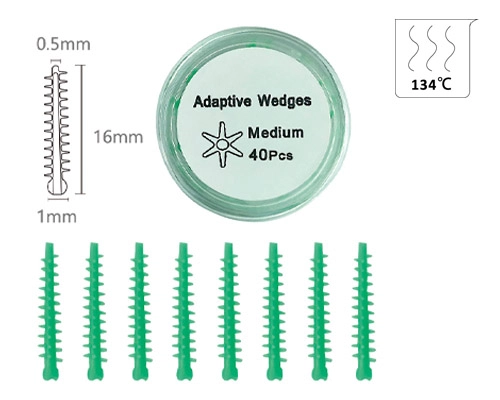



Cuñas dentales
- Material de alta calidad: Hecho de plástico médico, garantizar la seguridad y prevenir la contaminación con uso desechable
- Dimensionamiento versátil: Diseñado con diferentes tamaños: acomodar varios espacios interdentales
- Ajuste perfecto: Estas cuñas están diseñadas para encajar perfectamente entre los dientes, Ayudar en procedimientos precisos de restauración y llenado
Las cuñas dentales generalmente están hechas de madera, plástico, y caucho y se usan principalmente en tratamientos dentales para llenar los vacíos entre los dientes y evitar que el material se derrame durante el tratamiento. Durante la recuperación dental, Las cuñas dentales ayudan a formar nuevos puntos de contacto y mantener una posición de mordida normal. Las cuñas dentales también estabilizan la estructura del diente al prevenir el cambio de posición durante el tratamiento dental.
En odontología clínica, Las cuñas dentales sirven funciones terapéuticas duales. Durante los procedimientos de restauración dental, Facilitan la adaptación de la banda de matriz para garantizar un contacto proximal completo y evitar el voladizo del material en colocaciones de resina compuesta. El mecanismo de cuña crea una separación interproximal adecuada para una reproducción anatómica precisa mientras controla la morfología del margen gingival.
Ortodónticamente, Las cuñas dentales se emplean como herramientas complementarias para el movimiento de dientes controlados. Aplicando presión interradicular calibrada, Los médicos pueden lograr ajustes espaciales a nivel de micras durante las fases de alineación o estabilizar el reposicionamiento logrado durante los protocolos de retención.
Categoría de cuñas dentales

- Nueva yesa de plástico
- Ronda popa con un agujero
- Fácilmente de ser tomado,borde redondo con desapegado,Haga que las cuñas sean más flexibilidad para llenar las grietas de diferentes dientes
o 100 PCS/Box,550 cajas/CTN
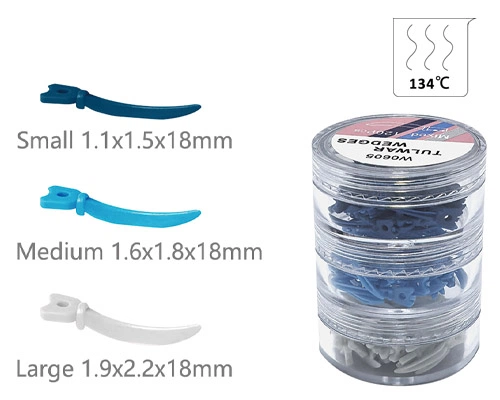
| Tamaño | Color | Longitud |
|---|---|---|
| Ss | azul | 17.8*1.7 mm |
| S | verde | 17.8*2.1 mm |
| METRO | amarillo | 17.8*2.45 mm |
| L | púrpura | 17.8*2.8 mm |

| Tamaño | Color | Longitud | Tamaño | Color | Longitud |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ss | azul | 10*1.8*1.6 mm | S | verde | 12*2*1.8 mm |
| METRO | amarillo | 14*2.2*2 mm | L | púrpura | 16*2.6*2.4 mm |

| Color | Longitud | Color | Longitud | Color | Longitud |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| naranja | 1.2*1.5*12 mm | púrpura | 2*2*15 mm | verde | 1.5*2*14 mm |
| amarillo | 1.3*2*16 mm | rosa | 1.5*2*16 mm | blanco | 1.3*1.5*14 mm |
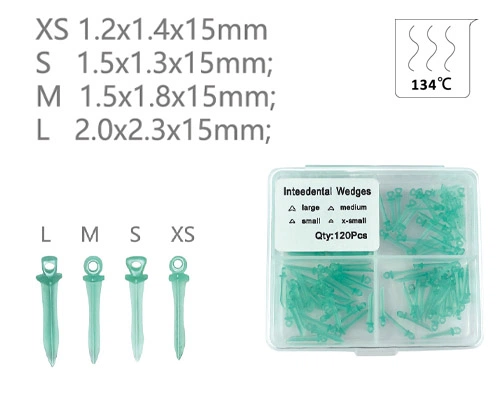


Las cuñas dentales juegan un papel muy crítico en la terapia dental moderna y son herramientas insustituibles para restaurar los dientes, ortodoncia, y otras disciplinas. Elija las cuñas dentales apropiadas mejorará la efectividad del tratamiento y reducirá a los pacientes.’ malestar.
Más detalles, Por favor contáctenos.
Productos de venta en caliente
Cuñas dentales: El "Pequeños asistentes" para restauración dental
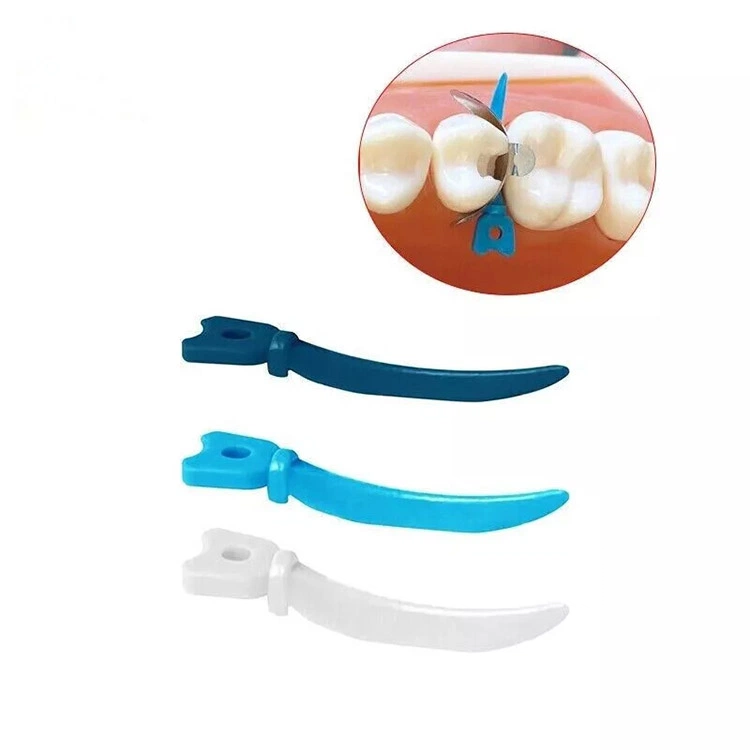
Cuñas para espacios dentales (también conocido como cuñas dentales) Son herramientas importantes utilizadas en el tratamiento bucal para aislar los dientes y proteger las encías.. Suele estar hecho de madera o plástico.. A pesar de su pequeño tamaño, Desempeña un papel importante en tratamientos como empastes dentales y restauraciones de carillas., especialmente en operaciones como resina compuesta, Empastes de cemento de iones de vidrio y amalgama de plata.. Insertando una cuña en el espacio interdental., El espacio entre los dientes se puede controlar eficazmente., las encías se pueden proteger, y la forma de la restauración se puede ajustar, aumentando así la tasa de éxito y la estabilidad del tratamiento..
La función de las cuñas dentales.
- Aislar las superficies adyacentes de los dientes.
Al empastar un diente o restaurar una caries en la superficie adyacente., Se inserta una cuña dental entre los dientes para separar la encía y fijar las Matrix Bands., Evitar que el material de restauración se adhiera al diente o encía adyacente.. - Proteger los tejidos periodontales.
Apretando ligeramente las encías, Se reduce el daño a los tejidos blandos causado por los instrumentos quirúrgicos., y se reduce el riesgo de sangrado de encías postoperatorio. - Conformación auxiliar
Asegúrese de que el material de restauración se adhiera estrechamente a las superficies adyacentes del diente para evitar complicaciones como protrusiones o impactación de alimentos después de la restauración..
Clasificación de cuñas dentales.
Cuña dental de madera
Fabricado con materiales de madera blanda como álamo y abedul., Tiene las ventajas de bajo costo y fácil poda.. El tamaño se puede ajustar según los espacios entre los dientes., y la madera tiene buena elasticidad natural, que puede reducir el daño a los tejidos periodontales de los dientes adyacentes. Sin embargo, Las desventajas de las cuñas dentales de madera son que tienen una fuerte absorción de agua, son propensos a la expansión y la deformación, y tener una fuerza relativamente baja. Se debe ejercer precaución al usarlos.
Cuña dental de plástico
Se hace comúnmente de materiales como el polietileno, polipropileno o nylon y se usa ampliamente en la odontología moderna. Según la diferente dureza, se puede clasificar como:
- Godas dentales de plástico rígidas: Alta resistencia y forma estable, Adecuado para situaciones con grandes huecos o bajo aflojamiento de los dientes adyacentes.
- Godas dentales de plástico elásticas: Tienen un cierto grado de elasticidad, puede adaptarse a los espacios irregulares, reducir la presión sobre las encías, y son adecuados para pacientes con encías sensibles o espacios estrechos.
Las ventajas comunes de las cuñas dentales de plástico son que son impermeables., No es fácil de romper, tener una superficie lisa, y reducir la adhesión al material de restauración. Dependiendo de sus formas, Las cuñas dentales de plástico vienen en varios tipos, como las con forma de espada., en forma de cuchillo, y tipos autoadaptativos. El tipo apropiado se puede seleccionar en función de las condiciones de las superficies adyacentes de los dientes..
Selección de materiales para cuñas dentales.
Requisitos de propiedades del material central:
- Biocompatibilidad: El material no debe tener ninguna reacción irritante con la mucosa oral., encías y tejidos dentales, evitando reacciones alérgicas o inflamación, especialmente en áreas que están en contacto prolongado con las encías. Debe cumplir con las normas de bioseguridad dental. (como ISO 10993).
- Propiedades mecánicas: Debe tener suficiente resistencia y tenacidad para soportar la presión durante el funcionamiento sin romperse fácilmente.. Al mismo tiempo, debe poder adaptarse a diferentes formas de espacios para evitar una rigidez excesiva que cause daños a los dientes o los tejidos periodontales..
- Estabilidad física: El material no debe absorber agua., deformarse o disolverse en el ambiente húmedo de la boca, evitando los cambios morfológicos causados por la saliva y afectando el efecto de restauración. Los materiales metálicos deben tener resistencia a la corrosión., y los materiales plásticos deben tener resistencia al envejecimiento.
- Comodidad operativa: El material debe ser fácil de recortar., dar forma o desinfectar, con una superficie lisa que reduce la adherencia al material de reparación, facilitando la extracción postoperatoria sin dejar residuos.
Seleccione diferentes cuñas dentales basadas en los materiales de restauración
- Llenado de resina compuesta: Seleccione cuñas dentales de plástico con superficies lisas que no sean propensas a la adhesión para evitar que la resina se adhiera a las cuñas y afecte la opresión de los bordes de la restauración.
- Relleno de amalgama de plata: Se pueden seleccionar cuñas dentales de madera o cuñas dentales de plástico rígidas. Debido a la pequeña contracción del volumen de la amalgama plateada durante el curado, El requisito de estabilidad para cuñas dentales es relativamente bajo.
- Relleno de cemento de iones de vidrio: Elija cuñas de plástico no absorbentes para evitar la expansión de las cuñas de madera debido a la absorción de agua, que puede afectar el efecto de curado del cemento.
Aplicación clínica de cuñas dentales
Pasos para colocar cuñas dentales
- Posicionando la brecha: Use pinzas para sostener la cuña dental, Alinee su punta con el espacio entre el diente afectado y el diente adyacente, y asegúrese de que el eje largo de la cuña dental sea paralela al eje largo del diente para evitar inclinar.
- Incrustación progresiva: Empuje suavemente el espacio con los dedos o un clip de cuña dental, Aplicar la fuerza gradualmente para evitar la fuerza repentina que puede causar daños en las encías o desplazamiento de los dientes adyacentes, hasta que el fondo de la cuña dental esté nivelado o ligeramente más bajo que la superficie oclusal.
- Examen de posición: Use una sonda dental para verificar la posición de la cuña dental para confirmar si las encías están comprimidas y empotradas, si la brecha interproximal está completamente expuesta, y si la cuña dental es estable.
Cooperación intraoperatoria y eliminación postoperatoria:
- Cooperación intraoperatoria: Al rellenar el material de restauración., Verifique periódicamente la posición de la cuña dental para evitar el desplazamiento de la cuña dental causado por la presión de llenado del material.. Si se utiliza resina compuesta curable por UV, Asegúrese de que la cuña dental no bloquee el área iluminada para evitar afectar el efecto de curado..
- extirpación postoperatoria: Después de que el material de restauración se haya solidificado, use pinzas para sujetar suavemente la parte inferior de la cuña dental y retírela lentamente a lo largo de la dirección de incrustación para evitar tirar que pueda dañar la restauración o las encías.. Después de la eliminación, la forma de las superficies adyacentes de la restauración, Se debe examinar el ajuste marginal y la condición gingival..
Precauciones al usar cuñas dentales
- Haga coincidir la forma de los espacios entre los dientes.
El tamaño de la cuña debe ser apropiado. Si es demasiado grande, puede causar presión sobre las encías. Si es demasiado pequeño, No puede sostener las bandas de matriz en su lugar. Seleccione la cuña apropiada basada en la forma tridimensional de los espacios entre los dientes. - Evite la operación violenta
Al insertar, Aplique presión lentamente para evitar la rotura de la cuña o causar daños a las encías. - Los pacientes especiales deben usar con precaución
Para pacientes con recesión grave de las encías o amplias brechas entre los dientes, Se recomienda usarlo en combinación con otros instrumentos. (tales como dar a las abrazaderas).
Preguntas frecuentes
Las cuñas dentales son herramientas auxiliares, generalmente hecho de madera o plástico, Se utiliza para fijar las bandas de matriz de superficie adyacentes durante los tratamientos restaurativos.
- Bandas de matriz estabilizadores: Previene el desbordamiento del material durante el llenado de resina.
- Proteger las encías: Presione las encías para contraerse y reducir el daño a los tejidos blandos causados por las operaciones de instrumentos.
- Mantener la relación adyacencia: Asegúrese de que el punto de contacto entre la restauración y el diente adyacente tenga forma natural.
Por material: cuñas de plástico (desechable), cuñas de madera (absorbente e hinchazón del agua).
Según el diseño: cuñas rectas, cuñas en forma de arco (adaptado a la curvatura anatómica de los dientes).
Por tamaño: Disponible en múltiples especificaciones como XS, S, METRO, y l, Para acomodar diferentes anchos de brecha de dientes.
- Daño de la goma: La operación inadecuada puede conducir a abrasiones o úlceras de la mucosa.
- Defecto de la restauración: La posición inadecuada de la cuña puede causar mala adyacencia o suspensión del cuerpo de llenado.