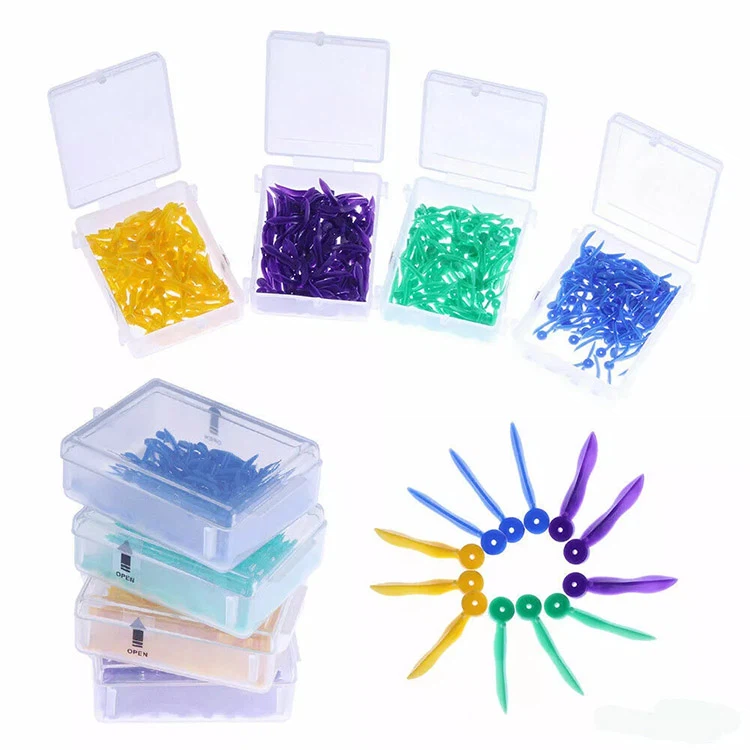
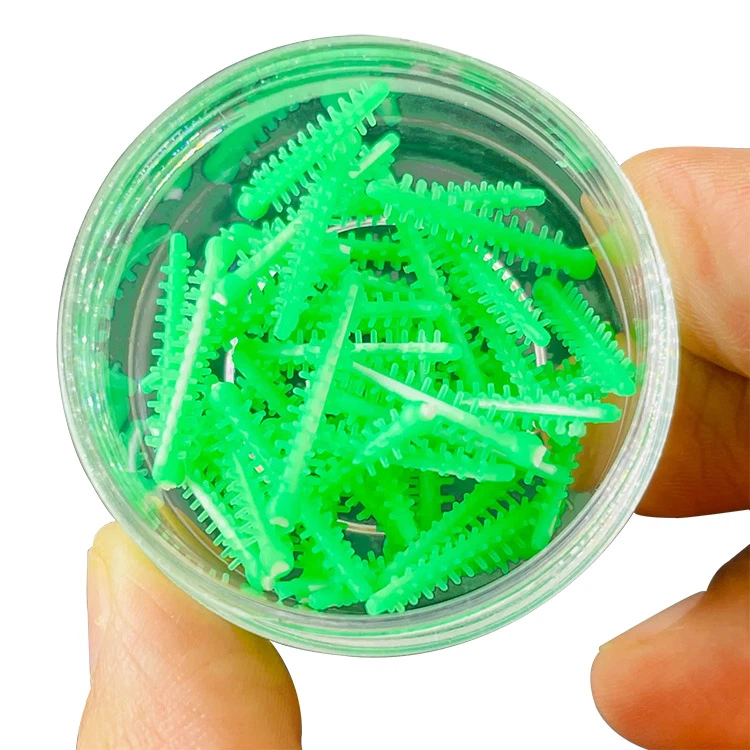
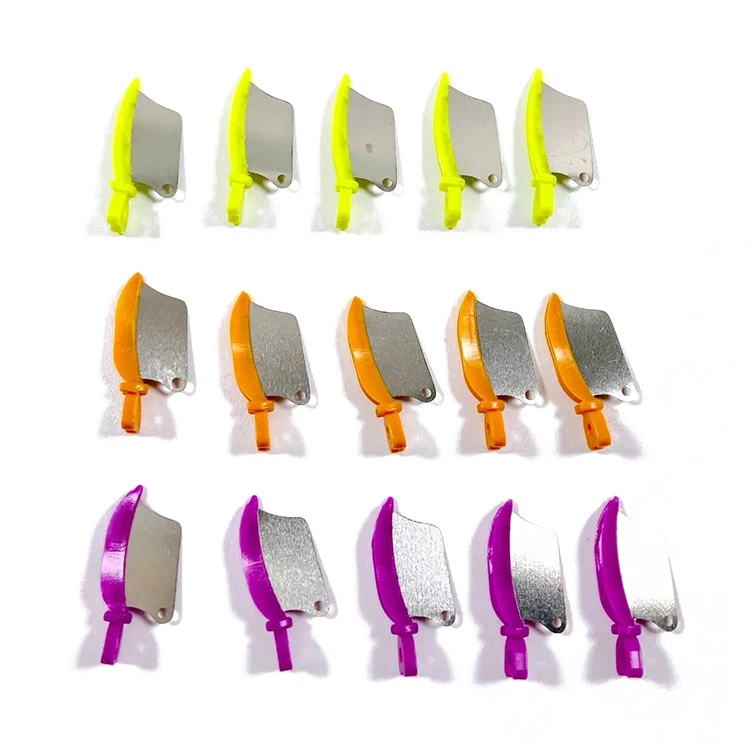
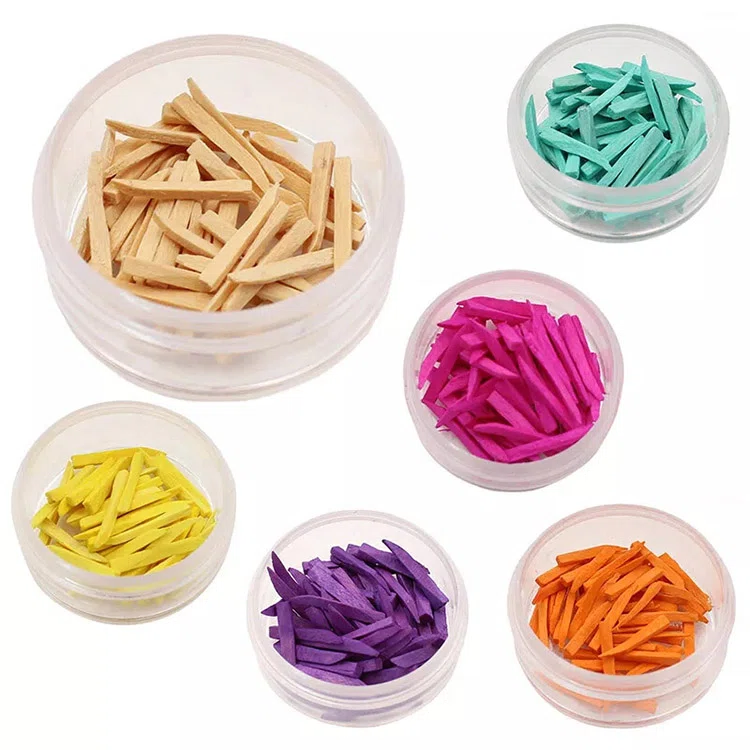
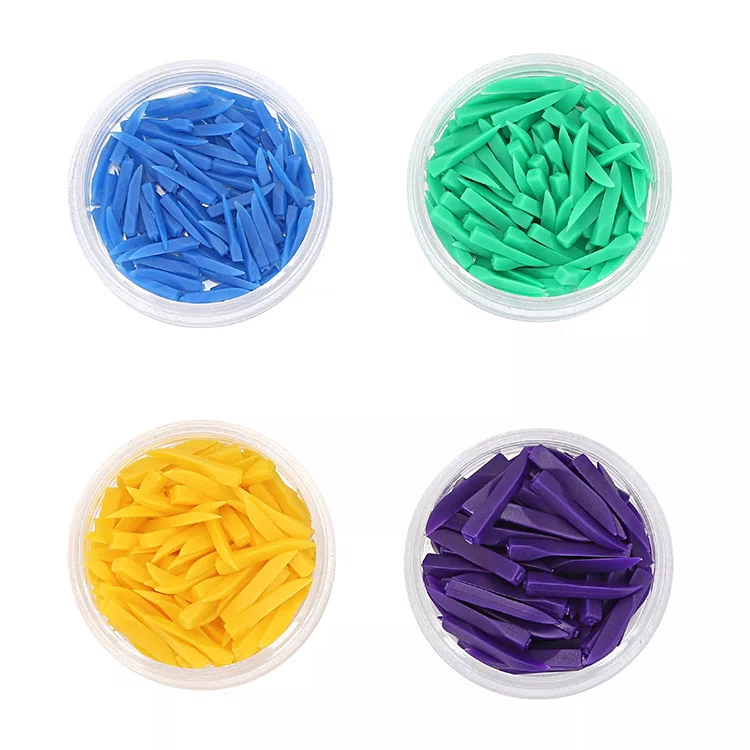
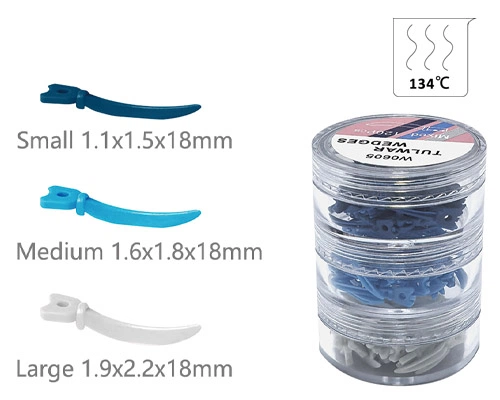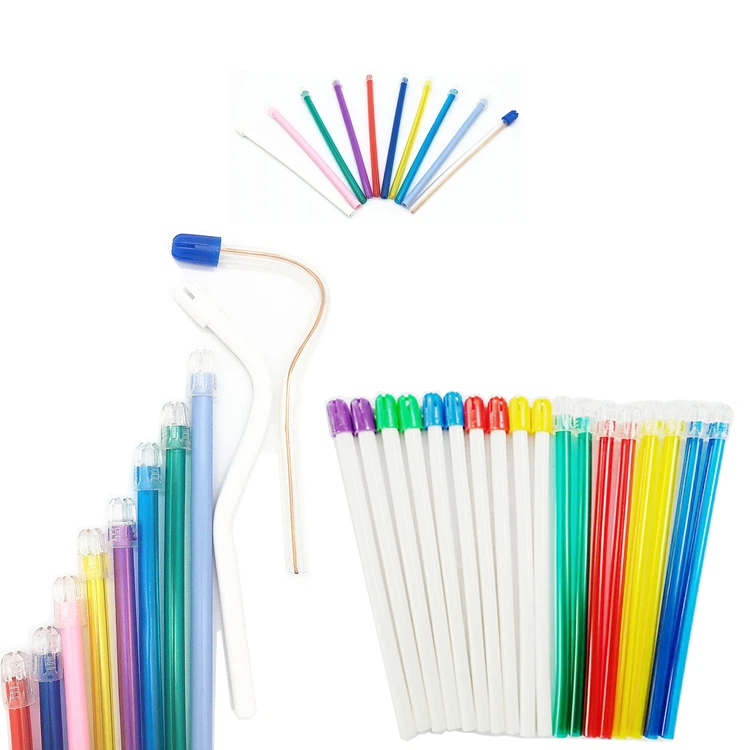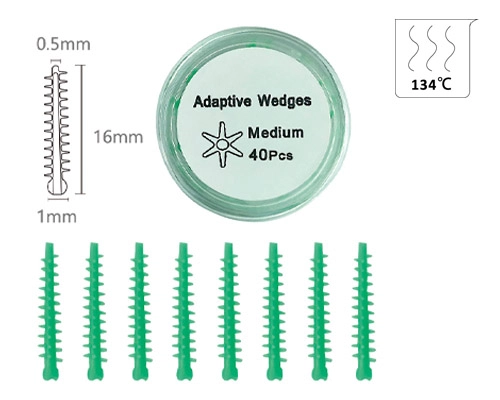



Zahnkeile
- Hochwertiges Material: Aus medizinischem Plastik, Sicherstellung und Verhinderung der Umweltverschmutzung mit verfügbarem Gebrauch
- Vielseitige Größe: Mit unterschiedlichen Größen entworfen - markieren Sie verschiedene interdentale Räume
- Perfekte Passform: Diese Keile sind so ausgelegt, dass sie eng zwischen den Zähnen passen, Unterstützung bei genauen Wiederherstellungs- und Füllverfahren
Zahnkeile bestehen in der Regel aus Holz, Plastik, und Gummi und werden hauptsächlich in Zahnbehandlungen verwendet, um die Lücken zwischen den Zähnen zu füllen und zu verhindern, dass Material während der Behandlung ausschüttet. Während der Zahnaufbereitung, Zahnkeile bilden dazu, neue Kontaktpunkte zu bilden und eine normale Bissposition aufrechtzuerhalten. Zahnkeile stabilisieren auch die Zahnstruktur, indem sie die Verschiebung der Position während der Zahnbehandlung verhindern.
In der klinischen Zahnheilkunde, Zahnkeile dienen zwei therapeutischen Funktionen. Während der Zahnrestaurationsverfahren, Sie erleichtern die Matrixbandanpassung, um einen vollständigen proximalen Kontakt zu gewährleisten und Materialüberhang in Verbundharzpraktika zu verhindern. Der Keilmechanismus erzeugt eine angemessene interproximale Trennung für eine präzise anatomische Reproduktion bei der Kontrolle der Gingivalrandmorphologie.
Kieferhopisch, Die Zahnkeile werden als Zusatzwerkzeuge für kontrollierte Zahnbewegungen eingesetzt. Durch Ausübung des kalibrierten interradikulären Drucks, Kliniker können räumliche Anpassungen auf Mikronebene während der Ausrichtungsphasen erreichen oder die erreichte Repositionierung während der Retentionsprotokolle stabilisieren.
Kategorie Zahnkeile

- Neue Plastikpoly-Kege
- Runde Heck mit einem Loch
- Leicht davon zu nehmen,runde Kante mit unordentlichem,Machen Sie die Keile mehr Flexibilität, um in verschiedenen Zähnen gefüllt zu sein
oder 100 PCs/Box,550 Kisten/CTN
| Größe | Farbe | Länge |
|---|---|---|
| Ss | Blau | 17.8*1.7 mm |
| S | Grün | 17.8*2.1 mm |
| M | Gelb | 17.8*2.45 mm |
| L | lila | 17.8*2.8 mm |

| Größe | Farbe | Länge | Größe | Farbe | Länge |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ss | Blau | 10*1.8*1.6 mm | S | Grün | 12*2*1.8 mm |
| M | Gelb | 14*2.2*2 mm | L | lila | 16*2.6*2.4 mm |

| Farbe | Länge | Farbe | Länge | Farbe | Länge |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| orange | 1.2*1.5*12 mm | lila | 2*2*15 mm | Grün | 1.5*2*14 mm |
| Gelb | 1.3*2*16 mm | Rosa | 1.5*2*16 mm | Weiß | 1.3*1.5*14 mm |
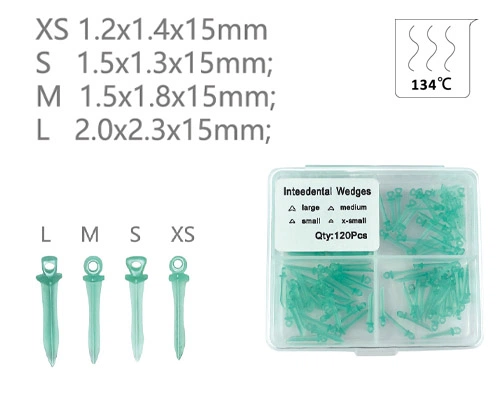


Zahnkeile spielen eine sehr entscheidende Rolle in der modernen Zahntherapie und sind unersetzliche Werkzeuge zum Wiederherstellen von Zähnen, Kieferorthopädie, und andere Disziplinen. Wählen Sie die geeigneten Zahnkeile, die die Effektivität der Behandlung verbessern und die Patienten verringern’ Unbehagen.
Weitere Details, Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns.
Zahnkeile: Der "Little Assistants" for Dental Restoration
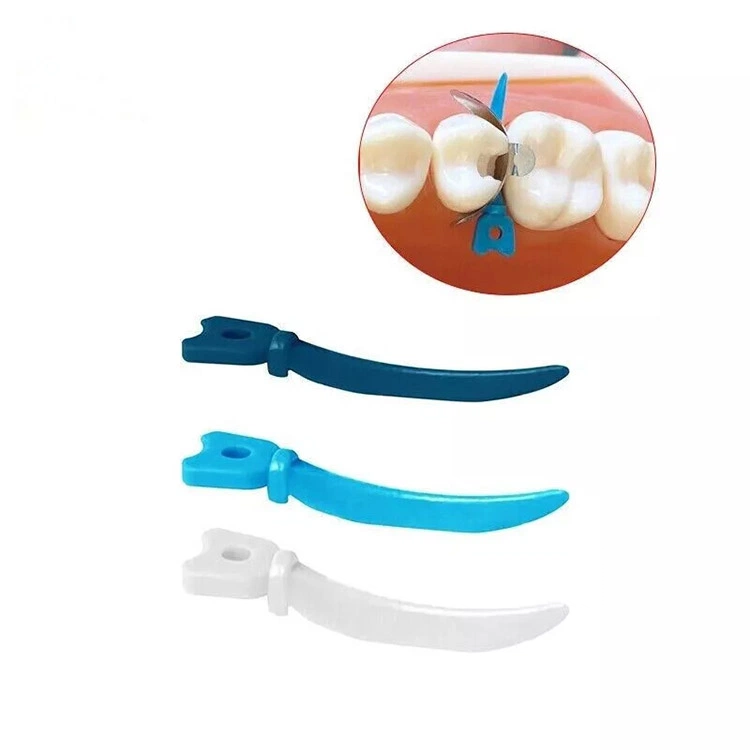
Dental gap wedges (also known as dental wedges) are important tools used in oral treatment to isolate teeth and protect gums. It is usually made of wood or plastic. Despite its small size, it plays a significant role in treatments such as dental fillings and veneer restorations, especially in operations like composite resin, glass ion cement and silver amalgam fillings. By inserting a wedge into the interdental gap, the space between teeth can be effectively controlled, the gums can be protected, and the shape of the restoration can be adjusted, thereby increasing the success rate and stability of the treatment.
The function of dental wedges
- Isolate the adjacent surfaces of teeth
When filling a tooth or restoring a caries on the adjacent surface, an dental wedge is inserted between the teeth to separate the gum and fix the Matrix Bands, preventing the restorative material from adhering to the adjacent tooth or gum. - Protect the periodontal tissues
By slightly squeezing the gums, the damage to soft tissues caused by surgical instruments is reduced, and the risk of postoperative gum bleeding is lowered. - Auxiliary shaping
Ensure that the restorative material adheres closely to the adjacent surfaces of the tooth to prevent complications such as protrusions or food impaction after restoration.
Classification of dental wedges
Wooden dental wedge
Made of softwood materials such as poplar and birch, it has the advantages of low cost and easy pruning. The size can be adjusted according to the gaps between teeth, and wood has good natural elasticity, which can reduce damage to the periodontal tissues of adjacent teeth. Jedoch, the disadvantages of wooden dental wedges are that they have strong water absorption, are prone to expansion and deformation, and have relatively low strength. Caution should be exercised when using them.
Plastic dental wedge
It is commonly made of materials such as polyethylene, polypropylene or nylon and is widely used in modern dentistry. According to different hardness, it can be classified as:
- Rigid plastic dental wedges: High strength and stable shape, suitable for situations with large gaps or low loosening of adjacent teeth.
- Elastic plastic dental wedges: They have a certain degree of elasticity, can adapt to irregular Spaces, reduce pressure on the gums, and are suitable for patients with sensitive gums or narrow Spaces.
The common advantages of plastic dental wedges are that they are waterproof, Nicht leicht zu brechen, have a smooth surface, and reduce adhesion to the restoration material. Depending on their shapes, plastic dental wedges come in various types such as sword-shaped, knife-shaped, and self-adaptive types. The appropriate type can be selected based on the conditions of the adjacent surfaces of the teeth.
Material selection for dental wedges
Core material property requirements:
- Biokompatibilität: The material should have no irritating reaction with the oral mucosa, gums and tooth tissues, avoiding allergic reactions or inflammation, especially in areas that are in prolonged contact with the gums. It must comply with dental biosafety standards (such as ISO 10993).
- Mechanical properties: It should have sufficient strength and toughness to withstand the pressure during operation without breaking easily. Gleichzeitig, it should be able to adapt to different gap shapes to avoid excessive rigidity causing damage to teeth or periodontal tissues.
- Physical stability: The material should not absorb water, deform or dissolve in the moist environment of the mouth, avoiding morphological changes caused by saliva and affecting the restoration effect. Metal materials should have corrosion resistance, and plastic materials should have aging resistance.
- Operational convenience: The material should be easy to trim, shape or disinfect, with a smooth surface that reduces adhesion to the repair material, facilitating postoperative removal without leaving any debris.
Select different dental wedges based on the restoration materials
- Composite resin filling: Select plastic dental wedges with smooth surfaces that are not prone to adhesion to prevent resin from adhering to the wedges and affecting the tightness of the edges of the restoration.
- Silver amalgam filling: Wooden dental wedges or rigid plastic dental wedges can be selected. Due to the small volume shrinkage of silver amalgam during curing, the stability requirement for dental wedges is relatively low.
- Glass ion cement filling: Choose non-absorbent plastic wedges to avoid the expansion of wooden wedges due to water absorption, which may affect the curing effect of the cement.
Clinical application of dental wedges
Steps for placing dental wedges
- Positioning the gap: Use tweezers to hold the dental wedge, align its tip with the gap between the affected tooth and the adjacent tooth, and ensure that the long axis of the dental wedge is parallel to the long axis of the tooth to avoid tilting.
- Progressive embedding: Gently push into the gap with your fingers or a dental wedge clip, applying force gradually to avoid sudden force that may cause gum damage or displacement of adjacent teeth, until the bottom of the dental wedge is level with or slightly lower than the occlusal surface.
- Position examination: Use a dental probe to check the position of the dental wedge to confirm whether the gums are compressed and recessed, whether the interproximal gap is fully exposed, and whether the dental wedge is stable.
Intraoperative cooperation and postoperative removal:
- Intraoperative cooperation: When filling the restorative material, regularly check the position of the dental wedge to prevent the displacement of the dental wedge caused by the filling pressure of the material. If UV-curable composite resin is used, ensure that the dental wedge does not block the illuminated area to avoid affecting the curing effect.
- Postoperative removal: After the restoration material has solidified, use tweezers to gently hold the bottom of the dental wedge and slowly remove it along the embedding direction to avoid pulling that may cause damage to the restoration or gum damage. After removal, the shape of the adjacent surfaces of the restoration, the marginal fit and the gingival condition should be examined.
Precautions for using dental wedges
- Match the shape of the gaps between teeth
The size of the wedge should be appropriate. If it is too large, it may cause pressure on the gums. If too small, it cannot hold the Matrix Bands in place. Select the appropriate wedge based on the three-dimensional shape of the gaps between teeth. - Avoid violent operation
When inserting, apply pressure slowly to avoid the wedge breaking or causing damage to the gums. - Special patients should use with caution
For patients with severe gum recession or wide gaps between teeth, it is recommended to use it in combination with other instruments (such as shaping clamps).
FAQs
Dental wedges are auxiliary tools, usually made of wood or plastic, used to fix the adjacent surface Matrix Bands during restorative treatments.
- Stabilizing Matrix Bands: Prevents material overflow during resin filling.
- Protect the gums: Press the gums to contract and reduce the damage to soft tissues caused by instrument operations.
- Maintain the adjacency relationship: Ensure that the contact point between the restoration and the adjacent tooth is naturally shaped.
By material: plastic wedges (Einweg), Holzkeile (water-absorbing and swelling).
According to the design: straight wedges, arc-shaped wedges (adapted to the anatomical curvature of teeth).
By size: Available in multiple specifications such as XS, S, M, and L, to accommodate different tooth gap widths.
- Gum damage: Improper operation may lead to mucosal abrasions or ulcers.
- Defect of the restoration: Improper position of the wedge may cause poor adjacency or suspension of the filling body.